HVAC Boiler System: What Is It and How Does It Work?

This Boiler blog is the fifth in a series of blogs that explores how Veris Industries products can be used to monitor and regulate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) applications.
What Is an HVAC Boiler System?
An HVAC boiler system burns combustible fuel or uses electricity to heat water. The hot water it produces then travels to faucets, showers, and appliances. It also provides heat for the building. This type of heating has existed for hundreds of years, and some outdated systems remain in place today.
However, the addition of automation devices, sensors, and other updates can drastically improve a boiler system's performance. Modern boilers are an effective and efficient HVAC solution for many industrial, residential, and commercial properties. They generally require less fuel and are quieter than furnace systems, and they may provide more consistent heating. Because they don't use forced air, they can also help improve indoor air quality.
How a Boiler Works
A boiler uses a combination of heat and pressure to increase the temperature of water. Like the chiller provides cooled water to the air handlers to condition the air, the boiler provides heated water to the air handlers to heat the air. Depending on the type of boiler and the application needs, the boiler can produce either hot water or steam. For our example, we will focus on a hot water producing system.
The boiler system consists of a feed water system, hot water distribution system, and a fuel system. The feed water system provides water to the boiler and regulates it automatically to meet the hot water demand. The hot water distribution system collects and controls the hot water produced in the boiler. The hot water is routed to the heating coils in the air handler. The fuel system regulates the burners that heat the water.
Inside the boiler, burners produce flames that heat metal tubes filled with water. Temperature and pressure are closely monitored and controlled to ensure safe operation of the boiler.
Types of Boilers
Although all boilers operate in the same basic way, they differ in terms of their design and fuel source. These are primary kinds of boilers in use today:
Fire-tube: These easy-to-operate boilers transport hot gasses from the heating source through tubes that travel through a water-filled chamber.
Water-tube: This boiler has an external heat source and water inside the tubes, making it highly efficient.
Electric: Electric boilers use electricity to generate heat and are often more expensive than other options.
Natural gas: Burning natural gas is the most common way to fuel a boiler.
Oil: Buildings without access to natural gas sometimes burn heating oil instead.
Condensing: Condensing boilers use the heat from exhaust gasses to heat water as it enters the boiler.
Combination: Common in residential spaces, combination boilers have both a water heater and a central heating boiler.
Knowing exactly what type of boiler you have is essential to your ability to properly use, maintain, and upgrade it.
Diagram of a Boiler System
HVAC Boiler Maintenance
To keep your boiler operating efficiently and safely for the people in your building, be sure to add it to your regular maintenance schedule. These tips will help keep it in good condition and limit expensive breakdowns:
-
Conducting inspections to identify damage or system flaws
-
Cleaning the boiler components
-
Checking pressure levels and looking for leaks
-
Adding lubricant as necessary
-
Confirming that the boiler is well-insulated
Depending on the boiler type, additional maintenance steps might also be necessary. For example, the Department of Energy recommends periodically cleaning the heat exchangers and testing the pressure-relief valves for hot water systems.
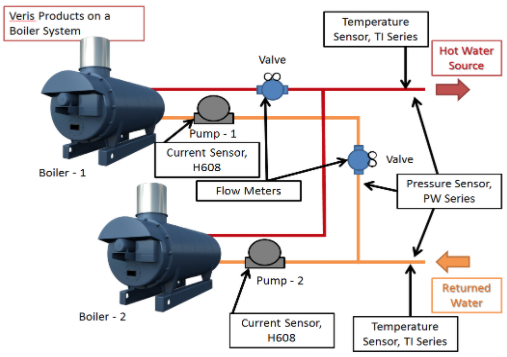
How a Boiler System Works with Veris Products
|
Product Family |
Why it is used on a Boiler |
|
Monitors the power used by the boiler. May assist with load shedding agreements. Excessive power usage may indicate a mechanical problem in the boiler pump motor(s). |
|
|
Wet DP used to monitor the differential pressure between water supply and return. Controls bypass valves to regulate flow based on demand. Provides a secondary proof of flow by monitoring the differential between supply and return air. Gauge pressure is used to monitor pressure on the line. Using a gauge pressure on both the supply and return will provide the data needed for the BMS to calculate the differential pressure. Low or high pressure readings may be an indicator of a mechanical failure in the system like a leak, pump failure, a clog, etc. |
|
|
Monitors run status on all pump motors. Can be used to detect on / off status, locked rotor, and overall pump status for proof of function / water flow. If the pump is drawing current, it is also pumping water. |
|
|
Used to monitor temp for heated water loop, helps to control the valve that determines water recirculation speed. Helps to determine pump speed, how much water needs to be returned, and is a main control point for the system. The value from this temp sensor can also be used for BTU calculations. |
|
|
Liquid Flow Meter monitors water flow in the supply and return lines of the heated water loop. BTU Meter is a flow meter combined with temperature sensors and can be used for energy measurements. The output is BTUs not a flow rate - its output is a measurement of the energy consumed by the boiler. It is also used to check the efficiency of the boiler. Clogs, malfunctioning pump, humidity changes, compressor cycling issues, can all be the causes of boiler inefficiency. Gas Flow Meter monitors the amount of natural gas or propane supplied to the boiler. |
Veris Industries offers a full line of sensing and monitoring products for HVAC boiler systems. Visit our website or book a virtual lunch with a Veris HVAC sensor expert to find products that are compatible with your boiler.
Read the entire HVAC series
Part 1: What are Air Handling Units (AHU)?
Part 2: What is a Water Chiller?
Part 3: What are Cooling Towers?
Part 4: What is a Variable Air Volume Box?
Part 5: What are HVAC Boiler Systems?





